Liver damage can happen gradually, often without noticeable signs until it becomes serious. Understanding the early symptoms of liver damage is crucial for timely intervention. Dr. Aswin Krishna emphasizes that recognizing these symptoms early can significantly improve treatment outcomes. Among the various causes, alcoholic liver disease early symptoms can be particularly deceptive, as individuals may not realize they have a problem until the damage is advanced. In this blog, we will explore the early signs, potential risks, and preventative measures associated with liver damage. By becoming informed, you can take proactive steps to safeguard your liver health.
What is Cirrhosis?
Cirrhosis is a severe liver condition characterized by the replacement of healthy liver tissue with scar tissue. This scarring can hinder the liver’s ability to function properly. As cirrhosis progresses, it can lead to various complications, including liver failure. The causes of cirrhosis often include chronic alcohol abuse, hepatitis infections, and fatty liver disease. Early detection and treatment are essential to slow down or prevent further liver damage. Cirrhosis often presents with few symptoms in its early stages, making it critical to be aware of the early symptoms of liver damage. Patients with cirrhosis may eventually experience fatigue, jaundice, and fluid accumulation in the abdomen, among other symptoms.
Early Symptoms
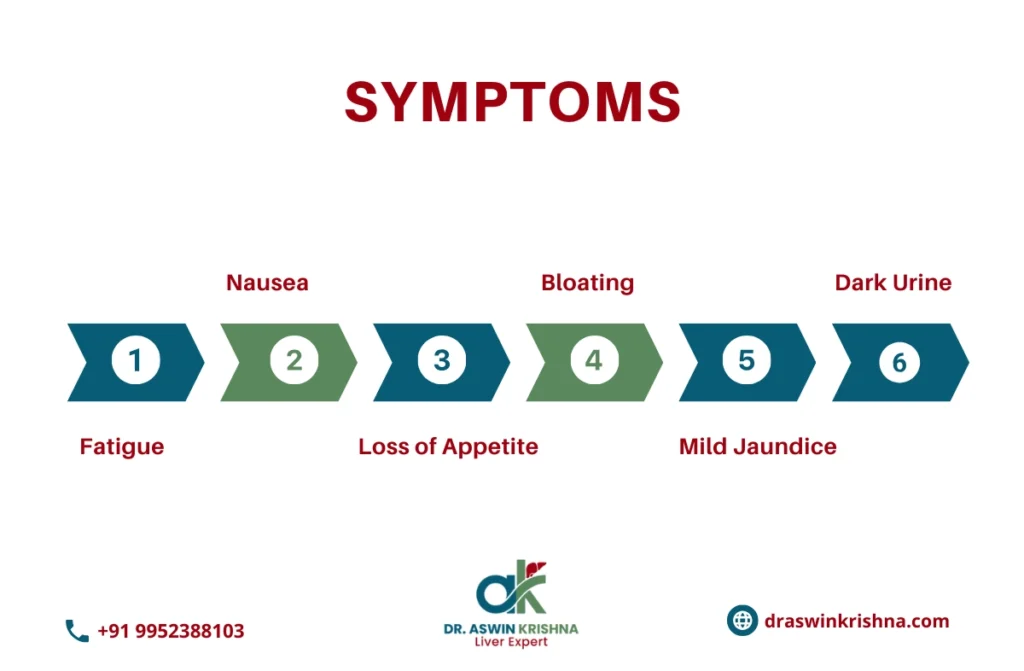
Recognizing the early symptoms of liver damage can help you seek medical attention before complications arise. Common early symptoms include:
- Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired or weak.
- Nausea: Frequent feelings of sickness or upset stomach.
- Loss of Appetite: Reduced desire to eat, leading to weight loss.
- Bloating: A sense of fullness or swelling in the abdomen.
- Mild Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin or eyes.
- Dark Urine: A noticeable change in urine color.
These can also be associated with alcoholic liver disease early symptoms. If you notice these signs, consult a healthcare professional promptly.
Later Symptoms
As liver damage progresses, you may start to notice more pronounced symptoms, including:
- Severe Jaundice: A deep yellowing of the skin and eyes.
- Swelling: Accumulation of fluid in the abdomen (ascites) or legs.
- Confusion: Mental changes due to the buildup of toxins in the blood.
- Easy Bruising: Increased tendency to bruise or bleed easily.
These later symptoms can indicate more serious liver conditions, requiring immediate medical intervention.
Red Flag Symptoms
Certain symptoms should prompt immediate medical attention:
- Severe Abdominal Pain: Pain that is sharp or persistent.
- High Fever: Elevated body temperature with other symptoms.
- Vomiting Blood: Blood in vomit or dark, tarry stools.
- Extreme Fatigue: Feeling excessively tired beyond normal levels.
Experiencing any of these symptoms can indicate a critical situation that needs urgent care.
Causes
Understanding the causes of liver damage can help in prevention:
- Alcohol Abuse: Excessive consumption can lead to alcoholic liver disease.
- Hepatitis: Viral infections can cause inflammation and damage.
- Obesity: Fatty liver disease related to obesity is increasingly common.
- Certain Medications: Some drugs can be toxic to the liver when used improperly.
Awareness of these causes can guide lifestyle changes to protect your liver.
Risk Factors
Several risk factors can increase the likelihood of liver damage:
- Family History: A genetic predisposition to liver disease.
- Unhealthy Diet: Diets high in fat and sugar can lead to fatty liver.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity contributes to weight gain.
- Age: Older individuals are at greater risk for liver disease.
Recognizing these risk factors can help you make informed decisions about your health.
Prevention
Preventive measures are essential for maintaining liver health:
- Limit Alcohol: Moderation is key to avoiding liver damage.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables supports liver function.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight.
- Vaccinations: Protect against hepatitis infections with vaccines.
Taking proactive steps can significantly reduce the risk of liver damage.
Treatment
Treatment for liver damage varies based on the underlying cause:
- Lifestyle Changes: Reducing alcohol intake and improving diet.
- Medications: Depending on the cause, medications may help manage symptoms.
- Surgery: In severe cases, liver transplants may be necessary.
- Monitoring: Regular check-ups to monitor liver function and health.
Early recognition of the early signs of liver and kidney damage is crucial for effective treatment.
Diagnosis and Tests
To diagnose liver damage, healthcare providers may conduct:
- Blood Tests: Check liver enzymes and function levels.
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasound, CT scans, or MRIs to assess liver condition.
- Biopsy: A small sample of liver tissue may be taken for analysis.
These diagnostic tools help identify the early signs of liver infection and determine the best course of action.
When to See a Doctor
It’s important to consult a doctor if you experience:
- Persistent Fatigue: Ongoing tiredness not linked to exertion.
- Changes in Urine Color: Dark urine or light-colored stools.
- Severe Abdominal Symptoms: Sharp pain or swelling in the abdomen.
Recognizing the early signs of liver and kidney damage can lead to timely intervention and better health outcomes.
Conclusion
Being aware of the early symptoms of liver damage is essential for maintaining liver health. Dr. Aswin Krishna reminds us that early detection and intervention can significantly improve the prognosis for those with liver conditions. Symptoms like fatigue, jaundice, and abdominal discomfort should not be ignored. If you notice these early signs of liver infection, seeking medical advice can help prevent further damage. Take charge of your liver health today!