Liver cancer, while more common in males, is a growing concern for females as well. Understanding the causes of liver cancer in females is critical for prevention, early detection, and timely treatment. In this blog post, we’ll explore the various causes, signs, and risk factors associated with liver cancer in women. Our goal is to break down complex medical information into easily understandable terms, making it simple to follow and empowering readers to take control of their health.
What is Liver Cancer?
Liver cancer is a condition where abnormal cells in the liver grow uncontrollably, forming tumors. It can start in the liver (primary liver cancer) or spread from other parts of the body (secondary liver cancer). Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of primary liver cancer, accounting for about 85% of cases. Other forms include cholangiocarcinoma and hepatoblastoma.
Is Liver Cancer a Common Disease?
Though liver cancer is less common than cancers like breast or lung cancer, its incidence is on the rise, particularly due to lifestyle factors and certain medical conditions. While it used to be more frequent in men, the number of cases in causes of liver cancer in females is growing. The rise is linked to increasing rates of conditions like hepatitis, obesity, and alcohol consumption, which all contribute to liver damage over time.
How Does Liver Cancer Affect My Body?
The liver plays an essential role in processing nutrients, filtering toxins, and producing proteins that help with blood clotting. Liver cancer disrupts these functions and can lead to several problems, such as:
- Jaundice: The skin and eyes turn yellow due to the liver’s inability to process bilirubin.
- Fatigue: Liver cancer can cause extreme tiredness and weakness.
- Abdominal pain: Pain in the upper right side of the abdomen is common as the tumor grows.
- Loss of appetite and weight loss: Advanced liver cancer often leads to significant weight loss and lack of appetite.
Causes of Liver Cancer in Females
Liver cancer, though less common in females compared to males, can still affect women. Understanding the causes of liver cancer in females is essential for prevention and early detection. Here are some key factors contributing to liver cancer in women:
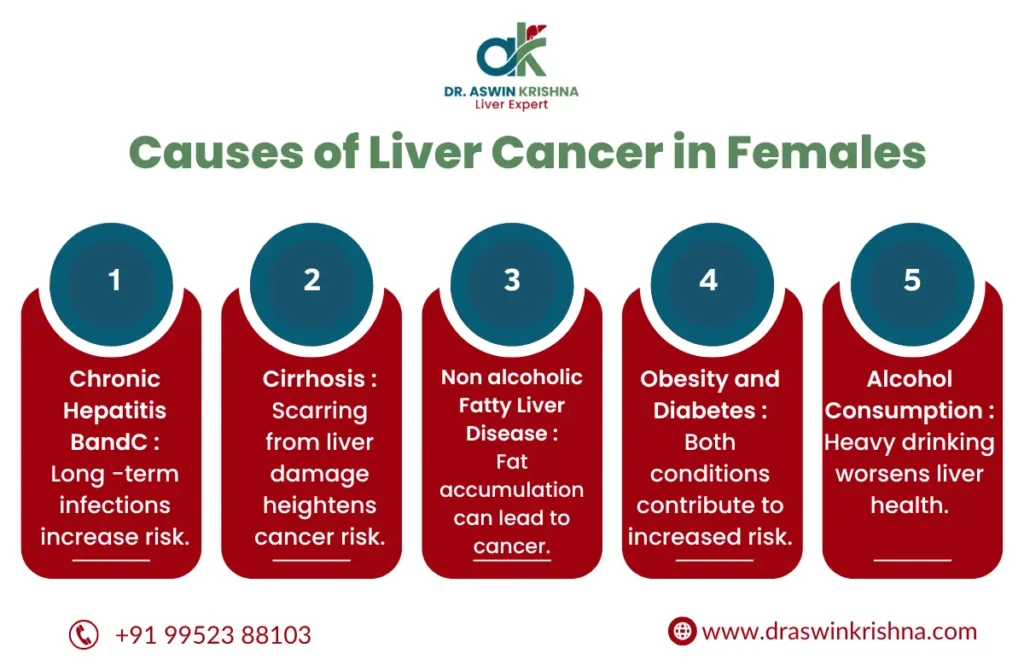
- Chronic Hepatitis B and C Infections: Chronic viral infections, especially hepatitis B and hepatitis C, are major risk factors for liver cancer in females. These infections can lead to liver cirrhosis, which increases the chances of developing cancer.
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): NAFLD is on the rise in women, particularly those who are obese or have diabetes. It can lead to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), a condition that increases the risk of liver cancer.
- Alcohol Consumption: Excessive alcohol consumption is a well-known cause of liver damage and cirrhosis, both of which are linked to liver cancer. Women are generally more susceptible to alcohol-induced liver damage than men.
- Obesity: Women who are overweight or obese have a higher risk of developing liver cancer, particularly due to the increased likelihood of fatty liver disease and insulin resistance.
- Hormonal Factors: Women who have used oral contraceptives or undergone hormone replacement therapy for extended periods may have an increased risk of developing liver tumors, though the association is still under study.
- Genetic and Family History: A family history of liver cancer can increase a woman’s risk, especially if there is a history of liver diseases like hepatitis or cirrhosis.
- Toxins and Chemical Exposure: Exposure to environmental toxins or chemicals, such as aflatoxins, can cause liver damage and lead to cancer. Women working in certain industries may be at a higher risk.
- Diabetes: Women with diabetes have an increased risk of liver cancer due to insulin resistance and the associated metabolic disturbances.
- Cirrhosis: Regardless of the underlying cause, liver cirrhosis—whether due to alcohol, viral infections, or fatty liver disease—is a significant factor in the development of liver cancer in females.
Understanding the causes of liver cancer in females can lead to better preventive measures, early detection, and more effective treatment. It’s important for women at risk to undergo regular screenings and maintain a healthy lifestyle to reduce their chances of developing liver cancer.
Signs and Symptoms
Liver cancer is often called a “silent” disease because symptoms may not appear until it is in the advanced stages. Common signs and symptoms to watch for include:
- Unexplained weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Upper abdominal pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- General weakness and fatigue
- Jaundice
- Swelling in the abdomen
Because these symptoms are often vague or associated with other conditions, it’s crucial to consult a doctor for regular check-ups, especially if you’re at higher risk.
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the risk of developing liver cancer, particularly in causes of liver cancer in females. These include:
- Hepatitis B or C infection: Long-term liver infections from these viruses significantly increase the chances of developing liver cancer.
- Cirrhosis: Scarring of the liver from conditions like hepatitis, alcoholism, or NAFLD is a major risk factor.
- Obesity: Excess body fat, particularly around the liver, increases the risk of NAFLD, which can lead to cancer.
- Alcohol consumption: Heavy drinking can cause liver inflammation and damage, eventually leading to liver cirrhosis and cancer.
- Diabetes: Type 2 diabetes is often associated with obesity and NAFLD, increasing the risk of liver cancer.
Understanding these risk factors of liver cancer can help to guide how to prevent liver cancer actions to lower your risk.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing liver cancer involves several steps, including:
- Blood tests: Doctors check for liver function and specific markers like alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), which can indicate liver cancer.
- Imaging tests: CT scans, MRIs, and ultrasounds help doctors visualize the liver and detect any abnormalities or tumors.
- Liver biopsy: In some cases, a small sample of liver tissue is taken to confirm the presence of cancer cells.
Treatment
The treatment for liver cancer depends on the stage of the disease and overall health. Common treatments include:
- Surgery: Removing the tumor or affected part of the liver. If caught early, surgery can sometimes cure the cancer.
- Liver transplant: In cases where the liver is severely damaged, a transplant may be necessary.
- Chemotherapy and radiation: These treatments aim to kill or shrink cancer cells, although they may cause side effects.
- Targeted therapy: This treatment focuses on specific molecules within cancer cells to stop their growth.
Screening for Liver Cancer
For individuals at high risk, screening for liver cancer is essential. Screening methods include:
- Regular blood tests: Monitoring liver enzymes and cancer markers.
- Ultrasounds or MRIs: These imaging tests can detect early signs of liver tumors.
Early detection through screening can save lives, as treatment is more effective in the early stages of the disease.
Prevention
Preventing liver cancer involves several key strategies. Knowing how can liver cancer be prevented can drastically reduce your risk. Here are some effective preventive steps:
- Vaccination: Hepatitis B vaccination is one of the most effective ways to prevent liver cancer caused by viral infections.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity can lead to liver damage and cancer. Regular exercise and a balanced diet can help keep your liver healthy.
- Limit alcohol intake: Reducing alcohol consumption or quitting altogether can help prevent cirrhosis, a major risk factor for liver cancer.
- Avoid environmental toxins: Be cautious about exposure to industrial chemicals and aflatoxins found in contaminated food.
These simple steps demonstrate how to avoid liver cancer by minimizing risk factors and promoting liver health.
Prognosis
The prognosis of liver cancer depends on the stage at which it is diagnosed. If detected early, the chances of successful treatment and long-term survival are significantly higher. However, if liver cancer is diagnosed at a later stage, the prognosis becomes more uncertain, as treatment options become limited. Regular screening for at-risk individuals improves the likelihood of early detection and better outcomes.
Conclusion
The causes of liver cancer in females are varied, ranging from viral infections and lifestyle factors to environmental exposures. However, by being aware of the risks and taking preventive measures, many cases of liver cancer can be avoided. Early detection through regular screening and prompt treatment can improve outcomes and offer a better quality of life. Now that you know the causes of liver cancer in females, take action today schedule a check-up, improve your lifestyle habits, and protect your liver health for the future.
Read also Probiotics For Liver Health.



