Liver transplant surgery is a life-saving procedure for patients suffering from liver failure, but the process is riddled with challenges in India. Despite advancements in medical technology, patients and healthcare systems still face various hurdles that complicate the process. The liver transplant challenges in India can be attributed to several factors including limited organ donors, high costs, and lack of awareness. Additionally, physical limitations, such as inadequate infrastructure in remote areas, can make access to transplantation difficult. These challenges not only delay treatments but also affect the success rates of transplants. This blog will explore the key liver transplant challenges in India and suggest potential ways forward.
Liver Transplant Challenges in India
The liver transplant challenges in India are multifaceted and stem from the complex nature of the transplant process. Among these are challenges in transplant process in india, which include inadequate medical facilities, organ rejection, and high post-surgery costs. These challenges make it harder for patients to receive timely and efficient care. In this section, we will explore the various difficulties faced by both patients and doctors during the transplantation journey.
Organ Donor Shortage
One of the biggest challenges facing liver transplant challenges in India is the severe shortage of organ donors. With the demand for liver transplants rising, the supply of organs simply isn’t enough. This scarcity is a major obstacle to successful liver transplantation in the country. Physical limitations such as public awareness and reluctance towards organ donation contribute significantly to this issue. Additionally, legal and ethical concerns around organ donation hinder the process. As a result, many patients have to wait for extended periods, and some may not receive a transplant in time.
Untimely Diagnosis, Faulty Referral, and Cultural Barriers
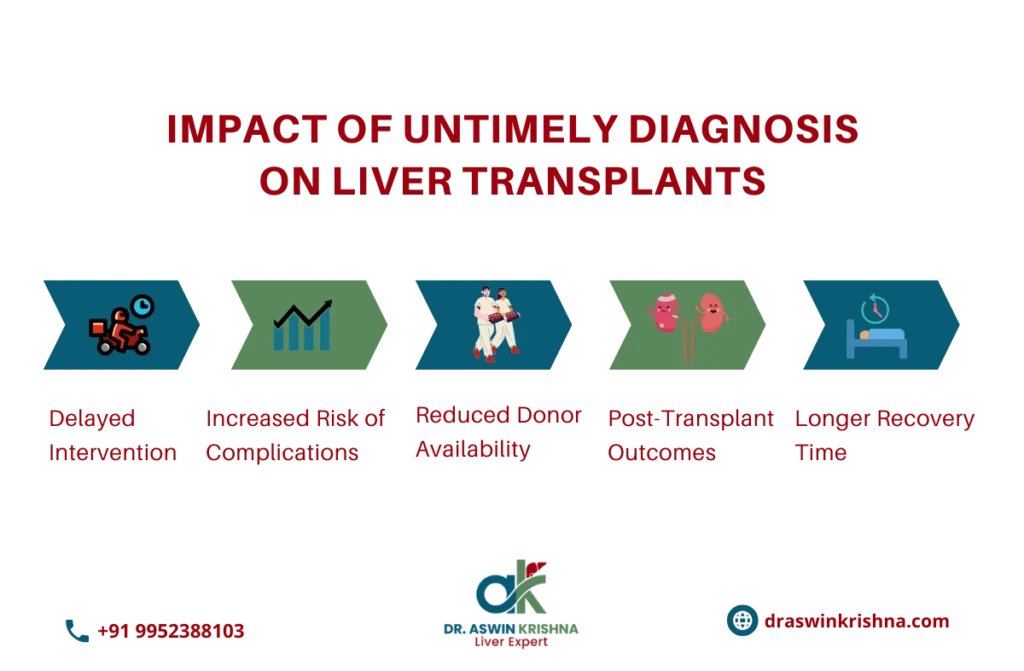
In India, liver transplant challenges in India are also linked to untimely diagnoses and faulty referrals. Many patients are diagnosed too late, reducing the success chances of a liver transplant. Additionally, cultural barriers such as mistrust in medical systems or lack of awareness can prevent patients from seeking treatment early. These delays often lead to the deterioration of the liver, making it less likely for a transplant to succeed. Addressing these issues requires improved medical outreach, better healthcare education, and faster referral systems.
Compromised Access to Liver Transplantation
Access to liver transplantation in india is compromised in India due to physical limitations and inadequate medical infrastructure. Patients in rural areas face difficulties in reaching transplant centers, where specialized care is available. Medication for surgery is also a key concern; many cannot afford the long-term immunosuppressive drugs required post-transplant. This lack of accessibility contributes to higher mortality rates among liver transplant candidates and results in delayed treatments. Improving healthcare access and affordability will be crucial to overcoming these challenges.
Financial Coverage
The high cost of liver transplant challenges in India is another major hurdle. Liver transplants can cost upwards of several lakhs, including pre-surgery consultations, post-operative care, and ongoing medication for surgery. For many families, this expense is beyond their means, making it difficult for patients to undergo the procedure. Public and private insurance schemes often do not cover the full cost, leaving patients in financial distress. Financial coverage, either through government support or private health plans, needs to be improved to make these life-saving procedures more accessible.
Graft Allocation Systems
A key liver transplant challenge in India is the graft allocation system, which is based on complex criteria such as urgency, compatibility, and waiting lists. While the allocation system aims to ensure fairness, it often leads to delays and inefficiencies. In many cases, liver transplant challenges in India are exacerbated by issues in graft distribution and prioritization, leaving some patients without timely access to the organs they desperately need. A more transparent and efficient graft allocation system is necessary for improving transplant outcomes.
Future Directions in Liver Transplantation
To tackle the liver transplant challenges in India, the future of liver transplantation in india needs innovation. Advances such as liver xenotransplantation and machine perfusion for deceased donor organs could offer new opportunities. These emerging technologies may reduce some of the current barriers, such as organ shortages and graft rejection, offering hope for patients in need of a liver transplant.
Tolerance and Immunosuppression Withdrawal
Challenges in transplant process in india often include managing immunosuppression and graft tolerance. Post-transplant, patients need to take medication to prevent organ rejection. However, long-term use of these drugs increases the risk of infections and cancer. The challenge of finding the right balance in immunosuppression withdrawal is a significant issue in liver transplant challenges in India. Better management protocols and advancements in immunosuppressive therapy will be necessary to reduce the risks while ensuring graft survival.
Increasing Donor Organs
Increasing the number of available donor organs is essential to overcome liver transplant challenges in India. Public awareness campaigns, incentivizing donations, and removing cultural taboos surrounding organ donation can help bridge the gap. Educational programs to address physical limitations in organ donation can also contribute to this effort. With more donors, waiting times can be reduced, and many more lives could be saved.
Machine Perfusion of Organs from Deceased Donors
Another promising solution for liver transplant challenges in India is machine perfusion of organs from deceased donors. This technique improves organ viability by using machines to supply oxygen and nutrients to the liver, preserving its function for longer periods. As the number of organ donors is limited, this technology can increase the pool of usable livers, allowing more patients to undergo successful liver transplants.
Liver Xenotransplantation
Liver xenotransplantation, or transplanting animal organs into humans, is another potential solution to liver transplant challenges in India. This experimental approach could address the chronic shortage of human donor organs. However, challenges such as immune rejection and ethical concerns need to be addressed. Ongoing research and advancements in xenotransplantation may eventually offer a solution to the severe organ shortage in India.
Expanding Indications – Non-Hepatocellular Carcinoma Liver Cancer
Expanding the indications for liver transplants, such as for patients with non-hepatocellular carcinoma liver cancer, could help more people in India access this life-saving treatment. Currently, liver transplantation is primarily reserved for cirrhosis and liver failure, but with better selection criteria and screening, more patients could benefit. This expansion would help address the growing demand for liver transplants in the country and improve outcomes for a broader group of patients.
Facilities for Liver Transplant in India
India offers world-class medical infrastructure for liver transplants, matching global standards at a fraction of the cost. Some of the top facilities include:
- Advanced Surgical Equipment: Minimally invasive techniques with state-of-the-art surgical tools.
- Highly Skilled Specialists: Renowned hepatologists and transplant surgeons with international training.
- Comprehensive Post-Operative Care: Specialized ICU facilities and 24/7 monitoring systems.
- Affordable Liver Transplants in India: Cost-effective treatment packages, making it a preferred destination for international patients.
These facilities ensure that Liver Transplantation in India remains accessible without compromising on quality.
The Liver Transplant Process
The liver transplant procedure in India follows a thorough, patient-centric approach:
- Pre-Transplant Evaluation:
- Comprehensive health assessments
- Matching donor compatibility
- Counseling for patients and family
- Surgical Procedure:
- Removal of the damaged liver
- Replacement with a healthy donor liver (from a living or deceased donor)
- Monitoring vital functions throughout the surgery
- Post-Transplant Care:
- Regular follow-up tests
- Immunosuppressive medications
- Nutritional and physical rehabilitation
Despite the country’s medical excellence, there are challenges in transplant process in India, including organ donor shortages and financial limitations for some patients.
Liver Transplant Statistics in India
India has seen remarkable improvements in liver transplant outcomes. Some key statistics include:
- Success Rate: Over 85% survival rate post-transplant
- Number of Procedures: Approximately 1,800 liver transplants are performed annually
- Cost-Effectiveness: Affordable liver transplants in India are typically 60-70% cheaper than those in Western countries
While progress has been significant, the challenges in transplant process in India—such as organ scarcity and post-operative complications—remain areas of ongoing improvement.
Conclusion
The liver transplant challenges in India are vast and multifaceted. While the country has made significant strides in improving healthcare infrastructure, many issues remain. From physical limitations and organ shortages to high costs and inefficient transplant systems, India must tackle these barriers to improve the accessibility and success rates of liver transplantation. Future innovations, like machine perfusion and xenotransplantation, show promise, but overcoming these challenges requires a coordinated effort across the medical, governmental, and societal levels. Addressing these liver transplant challenges in India will not only save lives but also bring hope to countless individuals in need of a liver transplant.
Read also Cadaveric Liver Transplant.