Managing chronic pain and inflammation is essential for improving quality of life, and meloxicam is a widely prescribed medication to achieve this goal. However, understanding the side effects of meloxicam is critical for safe and effective use. Dr. Aswin Krishna, a respected expert in the field, provides a comprehensive guide on meloxicam’s uses, benefits, and risks, including its impact on liver health with a focus on meloxicam and liver damage, meloxicam-induced liver toxicity, and meloxicam and fatty liver.
What is Meloxicam?
Meloxicam is a prescription nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) commonly used to manage arthritis-related conditions. Dr. Aswin Krishna explains its therapeutic role:
- Purpose: Meloxicam helps reduce pain, swelling, and stiffness caused by conditions like osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and juvenile arthritis.
- Convenience: It offers 24-hour relief with just one daily dose, making it a practical choice for long-term treatment.
While meloxicam is highly effective, understanding the side effects of meloxicam is essential for using it safely and effectively.
Why is Meloxicam Prescribed?
Meloxicam is favored by healthcare providers due to its effectiveness and safety profile. Dr. Aswin Krishna outlines the main reasons for its prescription:
- Pain Relief: It alleviates discomfort associated with joint inflammation, improving mobility and quality of life.
- Targeted Action: Meloxicam selectively inhibits COX-2 enzymes, which are responsible for inflammation, while sparing COX-1 enzymes that protect the stomach lining.
- Long-Lasting Effect: Its once-daily dosing ensures consistent relief without the need for multiple doses throughout the day.
Despite its advantages, awareness of the side effects of meloxicam is essential to minimize risks.
How Does Meloxicam Work?
Dr. Aswin Krishna explains how meloxicam targets the body’s inflammatory pathways:
- Selective Enzyme Inhibition: Meloxicam blocks cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) enzymes, which are responsible for producing prostaglandins that cause pain and swelling.
- Stomach Safety: By sparing COX-1 enzymes, meloxicam is less likely to cause stomach irritation or ulcers compared to older NSAIDs.
However, prolonged use can lead to complications, including meloxicam and liver damage, highlighting the importance of careful monitoring.
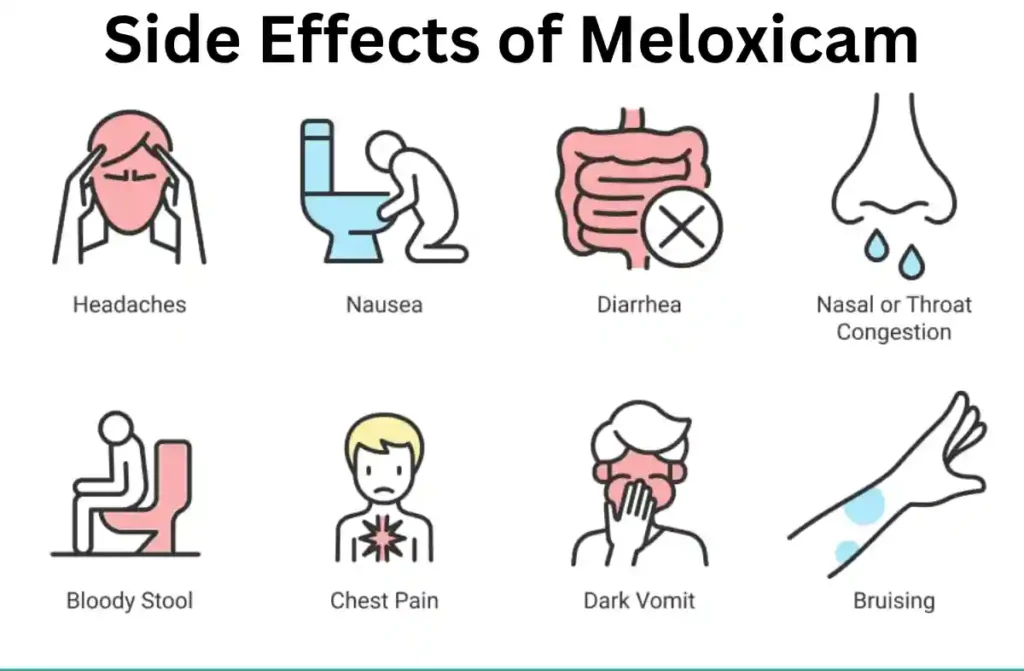
Meloxicam: More Common Side Effects
Meloxicam is a widely used NSAID prescribed for pain and inflammation. However, it is essential to understand the more frequent side effects of Meloxicam to ensure its safe use.
- Gastrointestinal disturbances: Among the most reported side effects of Meloxicam, nausea, heartburn, bloating, and abdominal pain are common. Some users may experience diarrhea or constipation, especially without food intake.
- Dizziness and headaches: Mild dizziness or persistent headaches can occur, especially when treatment begins. These effects often resolve but may require dose adjustments in sensitive individuals.
- Edema and fluid retention: Swelling in the ankles, legs, or hands may signal fluid retention, one of the common side effects of Meloxicam in adults, particularly in those with heart or kidney conditions.
- Skin issues: Mild rashes, itching, or sun sensitivity can occur. Though typically harmless, these skin effects can worsen in rare allergic reactions.
- Respiratory symptoms: Some individuals may experience a sore throat, nasal congestion, or cough, which should be monitored if persistent.
Meloxicam: Mild Side Effects
While usually non-threatening, the following side effects of Meloxicam can affect quality of life if not managed well:
- Taste changes and dry mouth: Some people report a metallic taste or dryness in the mouth. Drinking more fluids and chewing sugar-free gum may help reduce discomfort.
- Fatigue and drowsiness: A feeling of tiredness is one of the mild side effects of Meloxicam in adults, especially when starting treatment. It usually improves over time.
- Sweating and warmth: A warm sensation or increased sweating can occur, typically after a dose, but does not usually require discontinuation.
- Tinnitus: A ringing in the ears, though uncommon, may appear in sensitive individuals. It’s usually temporary and subsides with time.
- Mild digestive upset: Symptoms such as gas or slight bloating are usually relieved by taking the medication with meals.
Meloxicam: Serious Side Effects
Though infrequent, serious complications may arise and require immediate discontinuation and medical care.
- Gastrointestinal bleeding or ulcers: Severe stomach pain, black stools, or vomiting blood may indicate internal bleeding—one of the critical side effects of Meloxicam that can be life-threatening.
- Kidney impairment: Decreased urination, swelling, or electrolyte imbalances may result from impaired kidney function due to Meloxicam. This risk increases with dehydration and age.
- Meloxicam-induced liver toxicity: Some patients experience elevated liver enzymes, jaundice, or dark urine. This condition can indicate Meloxicam and liver damage, especially in long-term or high-dose users.
- Cardiac risks: Heart attack or stroke is a potential complication. Sudden chest pain, shortness of breath, or slurred speech may be early indicators.
- Allergic reactions: Hives, facial swelling, or difficulty breathing may suggest a severe immune reaction to Meloxicam and must be addressed immediately.
Meloxicam: Side Effects in Children
While Meloxicam can be prescribed to children for specific conditions like juvenile arthritis, caution is necessary due to their increased sensitivity.
- Gastrointestinal issues: Stomach cramps, vomiting, and diarrhea are more noticeable in pediatric patients, making hydration crucial during treatment.
- Behavioral and mood changes: Some children may become irritable or overly sleepy. These symptoms should be tracked for early intervention.
- Immune-related symptoms: Fever, rash, or flu-like signs may indicate adverse effects or an underlying infection.
- Liver concerns: Meloxicam-induced liver toxicity and Meloxicam and fatty liver are rarer in children but may occur in those with underlying liver conditions, requiring liver function monitoring.
Meloxicam: Side Effect Specifics
Understanding the underlying mechanisms of adverse reactions helps clarify why side effects of Meloxicam vary in severity.
- Gastrointestinal irritation: Meloxicam blocks protective prostaglandins, making the stomach lining more vulnerable to acid and injury, potentially leading to ulcers and bleeding.
- Hepatic stress: Meloxicam and liver damage may be seen in patients with long-term use or those with pre-existing liver conditions. Meloxicam-induced liver toxicity should be suspected in cases of jaundice or enzyme elevation.
- Fatty liver implications: In individuals with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), Meloxicam can aggravate inflammation. Meloxicam and fatty liver should be managed carefully with regular liver function tests.
- Renal and electrolyte disturbances: The medication can reduce renal blood flow, increasing creatinine and urea levels, particularly when combined with diuretics.
- Cardiovascular concerns: NSAIDs can raise blood pressure and increase the risk of clotting, especially in patients with heart disease.
Meloxicam and Hair Loss
Hair loss is not a widely documented adverse effect but has been reported by some users.
- Telogen effluvium: In some cases, Meloxicam may disrupt the normal hair growth cycle, leading to increased hair shedding, especially during stressful events or illness.
- Immunological effects: Since Meloxicam modulates inflammation, it may indirectly impact hair follicle function in sensitive individuals, particularly those with autoimmune disorders.
- Reversibility: In most cases, hair loss is temporary and resolves after discontinuation of the medication. Though not a primary issue, it can impact patient adherence.
Meloxicam: Side Effects in Older Adults
Meloxicam side effects in elderly individuals can be more intense due to decreased metabolism and organ reserve.
- Increased bleeding risk: Elderly patients are more prone to GI bleeding, especially with concurrent aspirin or corticosteroid use.
- Kidney concerns: Reduced renal clearance in older adults amplifies the risk of nephrotoxicity, one of the more dangerous side effects of Meloxicam in adults.
- Meloxicam and liver damage in older adults: Liver injury may present with vague symptoms such as confusion, poor appetite, or fatigue. Monitoring liver function is essential in prolonged therapy.
- Falls and dizziness: Even mild dizziness can be hazardous in this age group due to the risk of falls and fractures.
- Polypharmacy complications: Interactions with antihypertensives, anticoagulants, or diabetes medications are common, making Meloxicam side effects in elderly more unpredictable.
Meloxicam: Precautions
Proper precautions can reduce the likelihood and severity of adverse reactions.
- Evaluate pre-existing conditions: Patients with cardiovascular disease, kidney issues, ulcers, or fatty liver should use Meloxicam cautiously. It may exacerbate existing conditions or cause Meloxicam-induced liver toxicity.
- Drug interaction awareness: Combining Meloxicam with ACE inhibitors, blood thinners, or lithium increases the risk of complications, including kidney failure and bleeding.
- Regular testing: Monitoring kidney function and liver enzymes can help detect early signs of Meloxicam and liver damage or renal dysfunction before symptoms become severe.
- Hydration and dosage control: Maintaining proper hydration and using the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration minimizes the side effects of Meloxicam, especially in vulnerable populations.
- Avoid in late pregnancy: NSAIDs, including Meloxicam, may cause premature closure of the ductus arteriosus and are generally contraindicated in the third trimester.
Meloxicam and Fatty Liver: Is There a Connection?
Dr. Aswin Krishna examines the relationship between meloxicam and fatty liver, a condition characterized by excessive fat accumulation in the liver:
- Indirect Impact: While meloxicam does not directly cause fatty liver, its long-term use may exacerbate existing liver conditions by increasing liver stress.
- Monitoring: Regular liver imaging and blood tests are essential for detecting early signs of fatty liver disease or related complications.
Being proactive about liver health ensures safe and effective use of meloxicam.
Conclusion
Understanding the side effects of meloxicam is essential for anyone prescribed this medication. Dr. Aswin Krishna emphasizes the importance of consulting a healthcare provider, monitoring for warning signs, and undergoing routine tests to ensure its safe use. Whether addressing concerns about meloxicam and liver damage, meloxicam-induced liver toxicity, or meloxicam and fatty liver, staying informed empowers patients to use meloxicam safely and effectively.
Read also How To Detox Your Liver Naturally.



