Hepatitis C is a liver infection caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV), known for its stealthy progression and potential for severe liver damage. Understanding the facts about hepatitis C is essential for recognizing its risks, symptoms, and the importance of early diagnosis and treatment.
Facts about Hepatitis C
Facts about Hepatitis C reveal that it’s more than just a liver disease; it’s a global health concern affecting millions. This viral infection, primarily transmitted through blood-to-blood contact, can lead to severe liver damage, cirrhosis, and even liver cancer if untreated. The advancements in medical research have made it possible to cure Hepatitis C with antiviral medications, drastically reducing the risk of life-threatening complications. Public awareness and understanding of these facts are crucial for prevention and early treatment.
Transmission and Risk Factors
Understanding the Facts about Hepatitis C includes recognizing its transmission and risk factors. Hepatitis C, a blood-borne virus, primarily spreads through direct contact with infected blood. High-risk behaviors and conditions include:
- Intravenous drug use: Sharing needles is the most common way the virus spreads.
- Unregulated tattooing: Using non-sterile equipment can transmit the virus.
- Blood transfusion and organ transplants: Before rigorous screening was implemented, transfusions and transplants were significant transmission sources.
The risk of transmission emphasizes the need for preventive measures, such as using sterile medical equipment and practicing safe needle use, to combat the spread of Hepatitis C.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Delving into the Facts about Hepatitis C unveils critical insights into its symptoms and diagnosis. Hepatitis C often remains silent with few or no symptoms until liver damage becomes significant. When symptoms appear, they may encompass:
- Fatigue: A common early sign, often overlooked or attributed to other causes.
- Jaundice: Skin and eyes turning yellow, signifying liver trouble.
- Abdominal pain: Particularly in the liver area, accompanied by bloating or swelling.
For diagnosis, healthcare providers rely on specific blood tests that detect the presence of the hepatitis C virus or antibodies to the virus, often leading to further liver function testing to assess the extent of liver damage.
Treatment and Management
The Facts about Hepatitis C are pivotal in understanding its treatment and management. With the advent of direct-acting antivirals (DAAs), the approach to treating Hepatitis C has transformed, offering over a 90% cure rate. Crucial elements of treatment and management encompass:
- Antiviral medications: DAAs are the standard treatment, capable of clearing the virus in weeks.
- Regular monitoring: Liver function tests are crucial to gauge treatment response and manage progression.
- Lifestyle adjustments: Reducing alcohol intake and maintaining a healthy diet support liver health.
Effective management of Hepatitis C necessitates a combination of medical treatment, regular health monitoring, and lifestyle modifications to prevent liver damage and enhance quality of life.
Related Conditions and Complications
Facts about Liver Cancer
The Facts about Liver Cancer underscore the critical nature of this disease, which can be life-threatening if not detected and treated early. Liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma, is closely linked to chronic liver conditions, including hepatitis C and cirrhosis.
Key points include:
- Prevalence: It’s one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths globally.
- Risk factors: Chronic hepatitis, alcohol abuse, and aflatoxin exposure.
- Symptoms: Unintended weight loss, abdominal pain, and jaundice.
Recognizing these facts is vital for early diagnosis and effective treatment, emphasizing the need for regular health check-ups and liver function monitoring.
Facts about Fatty Liver
Facts about Fatty Liver reveal that it’s a common condition often linked to obesity, diabetes, and excessive alcohol consumption. Fatty liver disease can be non-alcoholic (NAFLD) or alcohol-related (AFLD).
Key points to consider:
- Prevalence: NAFLD is one of the most common forms of liver disease.
- Symptoms: Often asymptomatic, can progress to liver inflammation and scarring.
- Management: Weight loss, diet modification, and controlling blood sugar levels.
Understanding these facts is crucial for preventing progression to more severe liver conditions.
Interesting Facts about Cirrhosis
Interesting Facts about Cirrhosis shed light on this severe liver disease characterized by irreversible scarring of the liver tissue. Cirrhosis is often the result of chronic liver diseases, such as hepatitis and chronic alcohol abuse.
Key points include:
- Progression: It develops slowly, often over many years.
- Symptoms: Include fatigue, jaundice, and fluid accumulation.
- Complications: This can lead to liver failure and necessitates transplantation in advanced stages.
Knowing these facts emphasizes the importance of early intervention and lifestyle changes to manage liver health.
Interesting Facts about Liver Cancer
Interesting Facts about Liver Cancer highlight that liver cancer is one of the most aggressive and deadly forms of cancer. Its development is closely linked to chronic liver diseases like cirrhosis and hepatitis.
Key points include:
- Incidence: It ranks as the sixth most common cancer worldwide.
- Types: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) stands out as the most prevalent form.
- Risk factors: Chronic hepatitis B and C, alcohol abuse, and aflatoxin exposure.
Awareness of these facts is crucial for early detection and treatment, improving survival rates.
How to Avoid Getting Hepatitis C
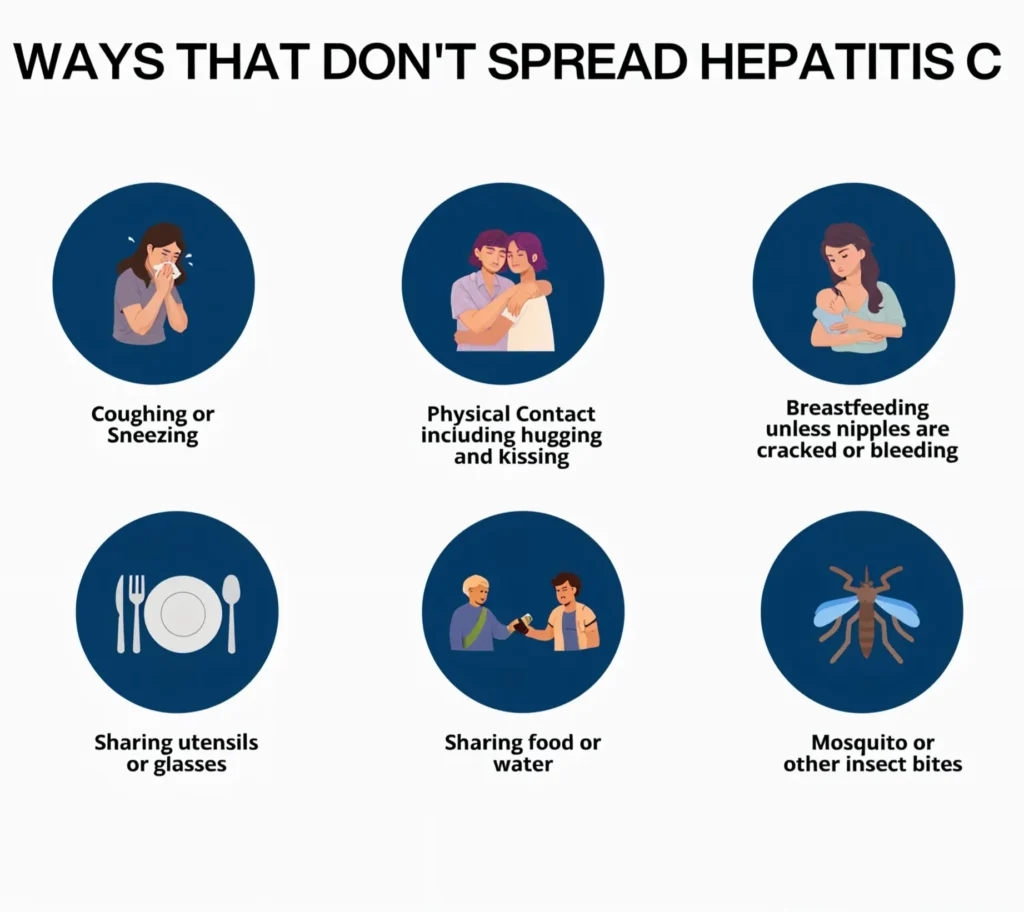
Preventing hepatitis C is possible, especially when you’re informed and proactive. The virus spreads through blood-to-blood contact, and knowing the risks can save lives.
Tips to Prevent Hepatitis C
- Avoid Sharing Needles: Injection drug use is a major transmission route.
- Practice Safe Sex: Use protection, especially with multiple partners.
- Be Cautious with Piercings & Tattoos: Always choose licensed professionals using sterile equipment.
- Don’t Share Personal Items: Razors, toothbrushes, and nail clippers can carry infected blood.
- Screen Blood Donations: Ensure transfusions are from tested and safe sources.
- Healthcare Safety: If you work in healthcare, follow protocols for handling blood.
These practices are crucial not only to prevent hepatitis C but also to reduce your risk of developing related liver complications. In fact, one of the interesting facts about liver cancer is that chronic hepatitis C is a leading cause.
What to Do If You Have Hepatitis C
Being diagnosed with hepatitis C isn’t the end—it’s the beginning of treatment and liver care. Early detection and lifestyle changes can drastically improve outcomes.
Steps to Take After Diagnosis
- Consult a hepatologist or infectious disease specialist: These experts can guide your treatment plan.
- Start Antiviral Treatment: Modern direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) can cure hepatitis C in over 95% of cases.
- Avoid Alcohol: Alcohol speeds up liver damage.
- Adopt a Liver-Friendly Diet: Choose low-fat, low-sodium foods rich in antioxidants.
- Stay Informed and Monitored: Regular blood tests and liver function tests are key.
- Notify Close Contacts: Help them get tested to avoid unnoticed transmission.
Among the lesser-known but crucial facts about hepatitis C is its “silent” nature—many people show no symptoms until significant liver damage has occurred. This silent progression is why it’s often connected to severe liver diseases, including cirrhosis and even liver cancer. In fact, one of the interesting facts about liver cancer is that it may remain undetected until the later stages, especially when caused by hepatitis C.
Conclusion
Embracing the facts about hepatitis C is essential for combating this silent yet potentially deadly virus. Understanding its transmission, risk factors, symptoms, and available treatments empowers individuals and communities to take proactive steps toward prevention and management. Early detection and modern therapeutic options offer a hopeful outlook for those affected, making knowledge a powerful tool in the global fight against hepatitis C.
Read also How to Prevent Liver Cirrhosis.